Adding Lineage
Why Would You Add Lineage?
Lineage is used to capture data dependencies within an organization. It allows you to track the inputs from which a data asset is derived, along with the data assets that depend on it downstream. For moreinformation about lineage, refer to About DataHub Lineage.
Goal Of This Guide
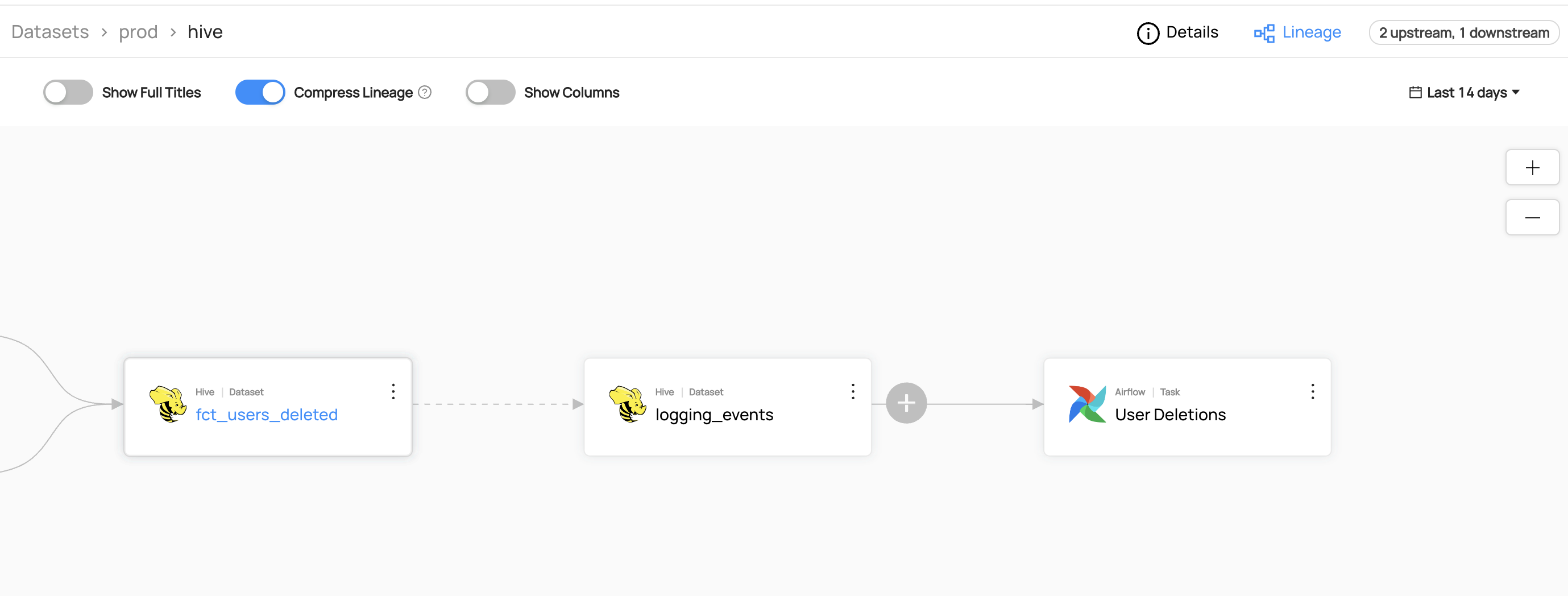
This guide will show you how to add lineage between two hive datasets named fct_users_deleted and logging_events.
Prerequisites
For this tutorial, you need to deploy DataHub Quickstart and ingest sample data. For detailed steps, please refer to Prepare Local DataHub Environment.
Before adding lineage, you need to ensure the targeted dataset is already present in your datahub. If you attempt to manipulate entities that do not exist, your operation will fail. In this guide, we will be using data from sample ingestion.
Add Lineage With GraphQL
Please note that there are two available endpoints (:8000, :9002) to access GraphQL.
For more information about the differences between these endpoints, please refer to DataHub Metadata Service
GraphQL Explorer
GraphQL Explorer is the fastest way to experiment with GraphQL without any dependencies.
Navigate to GraphQL Explorer (http://localhost:9002/api/graphiql) and run the following query.
mutation updateLineage {
updateLineage(
input: {
edgesToAdd: [
{
downstreamUrn: "urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,logging_events,PROD)"
upstreamUrn: "urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,fct_users_deleted,PROD)"
}
]
edgesToRemove: []
}
)
}
Note that you can create a list of edges. For example, if you want to assign multiple upstream entities to a downstream entity, you can do the following.
mutation updateLineage {
updateLineage(
input: {
edgesToAdd: [
{
downstreamUrn: "urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,logging_events,PROD)"
upstreamUrn: "urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,fct_users_deleted,PROD)"
}
{
downstreamUrn: "urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,logging_events,PROD)"
upstreamUrn: "urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,fct_users_created,PROD)"
}
]
edgesToRemove: []
}
)
}
For more information about the updateLineage mutation, please refer to updateLineage.
If you see the following response, the operation was successful:
{
"data": {
"updateLineage": true
},
"extensions": {}
}
CURL
With CURL, you need to provide tokens. To generate a token, please refer to Generate Access Token.
With accessToken, you can run the following command.
curl --location --request POST 'http://localhost:8080/api/graphql' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer <my-access-token>' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' --data-raw '{ "query": "mutation updateLineage { updateLineage( input:{ edgesToAdd : { downstreamUrn: \"urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,fct_users_deleted,PROD)\", upstreamUrn : \"urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,logging_events,PROD)\"}, edgesToRemove :{downstreamUrn: \"urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,fct_users_deleted,PROD)\",upstreamUrn : \"urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,fct_users_deleted,PROD)\" } })}", "variables":{}}'
Expected Response:
{"data":{"updateLineage":true},"extensions":{}}
Add Lineage With Python SDK
You can refer to the related code in lineage_emitter_rest.py.
import datahub.emitter.mce_builder as builder
from datahub.emitter.rest_emitter import DatahubRestEmitter
# Construct a lineage object.
lineage_mce = builder.make_lineage_mce(
[
builder.make_dataset_urn("hive", "fct_users_deleted"), # Upstream
],
builder.make_dataset_urn("hive", "logging_events"), # Downstream
)
# Create an emitter to the GMS REST API.
emitter = DatahubRestEmitter("http://localhost:8080")
# Emit metadata!
emitter.emit_mce(lineage_mce)
We're using the MetdataChangeEvent emitter to change entities in this example.
For more information about the MetadataChangeEvent, please refer to Metadata Change Event (MCE)
Expected Outcomes
You can now see the lineage between fct_users_deleted and logging_events.